What is Water Hardness?
Simple definition of hardness of water is the amount of calcium & magnesium ions present in water. It is divided in two parts carbonate or temporary hardness and non-carbonate or permanent hardness.
It is a major source of scale in water systems i.e. boiler water & cooling water system. Softening is a popular method for removal of hardness from water.
Let us discuss both the types of water hardness in detail.
#1. Carbonate or Temporary Hardness
Carbonate and bicarbonate ions are responsible for this type of water hardness.It is also known as temporary hardness because it removes from water when we boil the water.
When we boil the water carbonate & bicarbonates ions are present in water decomposes & insoluble carbonate is reformed.Boiling the water causes the precipitation of calcium and magnesium carbonate so that, calcium and magnesium ions are remove from water.
Example: CaCO3, MgCO3, Ca(HCO3)2, Mg(HCO3)2
#2. Non-Carbonate or Permanent Hardness
Chloride and Sulfate (non-carbonate) ions are responsible for this type of water hardness.It is also known as permanent hardness because it isn’t remove from water by boiling it.
It is only remove from water either by softening or demineralization process.
Example: CaCl2, MgCl2, CaSO4, MgSO4
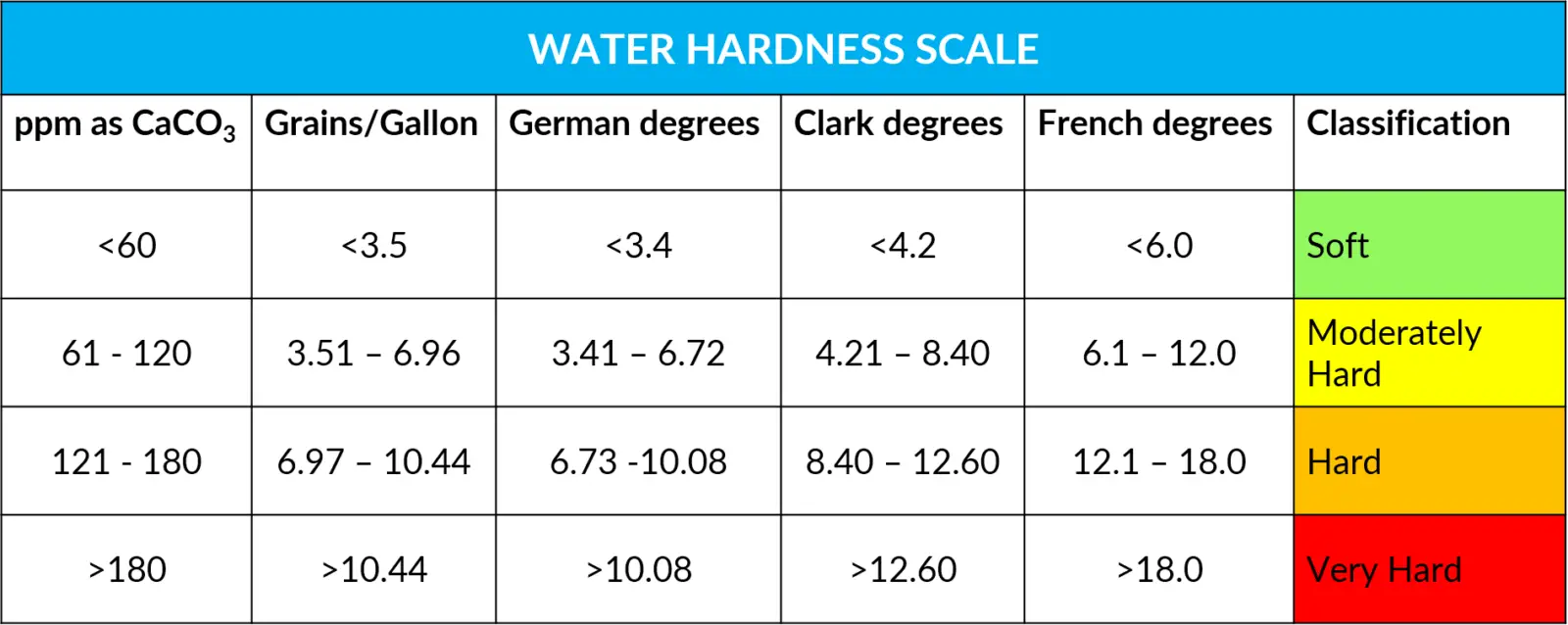
Water Hardness Scale:
As a general rule for classification of hardness, Water having hardness below 60 ppm is considered as soft water,61 ppm to 120 ppm as moderately hard; 121 ppm to 180 ppm as hard & above 181 ppm as very hard.
Water Hardness Measurement:
Analysis of Water harness divide in three parts namely total hardness,calcium hardness & magnesium hardness.
Total hardness is a sum of calcium & magnesium hardness.
Total Hardness = Calcium Hardness + Magnesium Hardness
In order to determine total hardness ammonia buffer solution is added to the sample to maintain the pH of around 11. Then Eriochrome Black T indicator is added so the wine red color is developed in the sample.
After that titrate the sample against EDTA solution and sample color will change from wine red to blue. This is the end point of total hardness titration.
Determine the calcium hardness by titration sodium hydroxide solution is added to the sample to maintain pH & then murexide indicator is added. Sample color turns into pink & titrate the sample against EDTA solution this time sample color will change from pink to purple. This is the end point of calcium hardness test.
Magnesium hardness is the difference of total hardness & calcium harness value. It is determined by subtracting calcium hardness value from total hardness value.
Magnesium Hardness = Total Hardness – Calcium Hardness
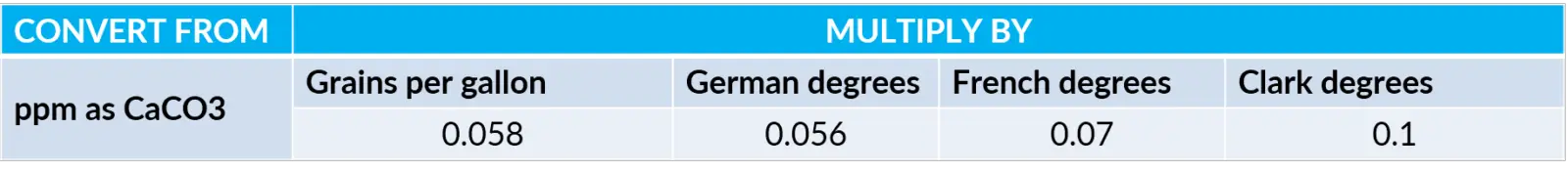
Water Hardness Conversion:
In Conclusion, Water hardness is a major source of scale in water treatment system. It is very essential to remove it from water by selecting proper water treatment program.





