Oxygen Pitting Corrosion in boiler:
The presence of dissolved oxygen in boiler system is responsible for pitting corrosion. Water acts as a cathode of any corrosion cell to depolarize, thereby sustaining the corrosion process. The most familiar form of oxygen attack in boilers and condensate systems is oxygen pitting.
Oxygen pitting is a problem for both ideal as well as boiler which is in operating conditions. Super heater & reheater tubes for ideal boiler and economiser & feedwater heaters for operating boiler are the favorable attack places.
Required conditions for oxygen pitting:
- A reactive metal that will corrode – typically carbon steel
- An electrolyte to conduct the current – feedwater, boiler water or condensate
- An oxidizing agent – dissolved oxygen
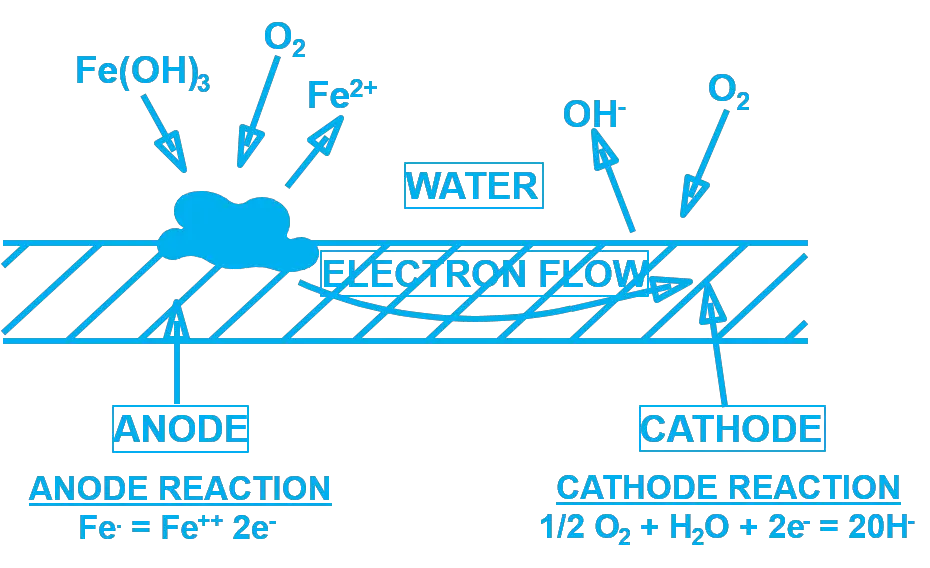
The presence of oxygen is also a necessary component of other corrosion mechanisms; however, its role is less obvious.
Dissolved oxygen is essential to ammonia corrosion of copper alloy condenser tubes and contributes to chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking of austenitic stainless steels in steam generators.
Mechanism of Oxygen Pitting :
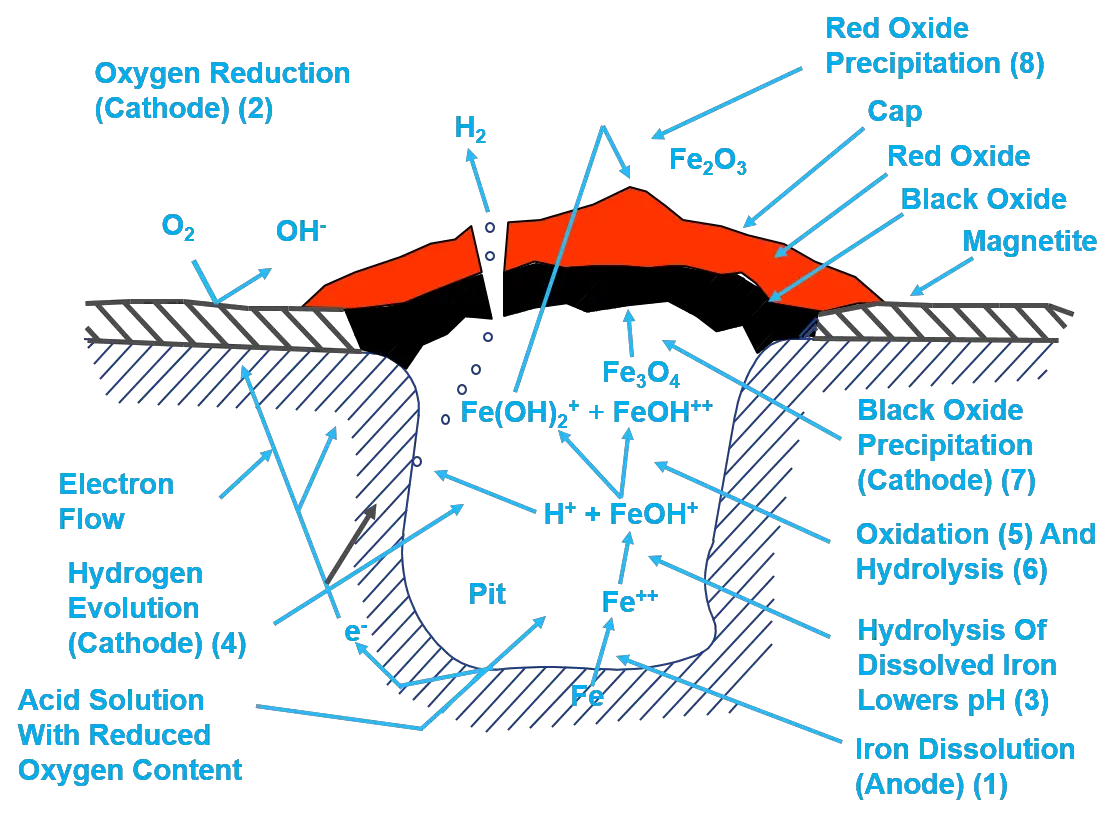
Characteristics of oxygen pitting corrosion:
- Corrosion Rate Doubles With Every 18 F (10 C) Increase In Water Temperature
- Highly Localized Metal Loss
- Rapid Failure
- Pit Formation
- Economizer Tubes Are Vulnerable
Therefore, it is essential that the dissolved oxygen concentration to be kept at the lowest feasible and economically justifiable level throughout all steam generating systems regardless of type, size or pressure.
Normally, Dissolved oxygen level of <5 ppb in deaerator outlet water is the safe range.
This requirement grows more critical as the operating pressure increases and as systems become larger, because the cost and danger of equipment failure increase proportionately.
Where do you see oxygen pitting corrosion in boiler?
- Deaerator below water line
- Economiser inlet area
- Feed water heater
- Superheater
- Reheater
- Water tube boiler: Drum water lines, belly plates, tube ends, feed water line, mud drum
- Fire tube boiler: tube sheets, especially weld seams
There are 7 different types of pitting corrosion.
In conclusion, Oxygen pitting involves highly localized metal loss, and potential for rapid equipment failure. It is also major cause of failures in low pressure boiler systems.
Protective magnetite layer(Fe3O4),Proper mechanical deaeration followed by chemical deaeration with proper oxygen scavenger chemical are the remedies of pitting corrosion in boiler.
It is important to note that mechanical deaeration must be applied not only to the makeup water stream but also to any return condensate, especially if the condensate return system operates under a vacuum.
